Article • 2 min read
ChatGPT vs. Bard
ChatGPT and Google Bard provide similar services but work in different ways. Read on to learn the potential benefits and limitations of each tool.
Door Hannah Wren, Staff Writer
Laatst gewijzigd September 5, 2023
Businesses are rethinking how they get things done thanks to advances in generative artificial intelligence (AI). Content creators, coders, and many others can use AI to improve their work quality and productivity.
ChatGPT and Google Bard are the two generative AI products that are getting the most buzz, and businesses want to know which one is best for their needs. We tested ChatGPT vs. Bard in key performance areas to help businesses decide exactly that. Read on to learn when you should use each service.
- What are ChatGPT and Google Bard?
- Bard vs. ChatGPT at a glance
- ChatGPT vs. Bard: A detailed comparison
- ChatGPT vs. Bard pricing
- Pros and cons of Bard and ChatGPT
- Is ChatGPT or Bard better for your business?
What are ChatGPT and Google Bard?
ChatGPT and Bard are generative AI products, meaning they respond to user prompts without the assistance of a human on the other end. ChatGPT and Bard aren’t ready to be used as customer-facing tools on their own, but generative AI models can enhance the performance of a company’s specialized bots.
OpenAI developed ChatGPT, which uses a Microsoft supercomputing platform to run its systems. Bard was created by Google and launched soon after ChatGPT made its debut.
Both AI tools use large language models (LLMs) to learn from datasets of text and code to inform their responses. The products can create content, answer questions, and translate text, but the quality of their performance can vary.
Bard vs. ChatGPT at a glance
ChatGPT | Google Bard | |
|---|---|---|
| Price | Free Plus: $20 per month | Free |
| Language model | Free: GPT-3.5 Plus: GPT-4 | Pathways Language Model (PaLM 2) |
| Data sources | ChatGPT is trained on a dataset pulled from sources like Wikipedia, scientific journals, and news articles pre-September 2021. ChatGPT Plus has internet access through plugins. | Bard is trained on Infiniset, a curated collection of internet content. Bard has internet access through Google. |
| User-friendliness | Accessible to users of all skill levels | Accessible to users of all skill levels |
| Use case | Content generation, content revision, writing/debugging code, language translation ChatGPT Plus can provide content summaries, information on current events, and image surfacing. | Content summaries, content generation, information on current events, language translation, image surfacing |
ChatGPT vs. Bard: A detailed comparison
Whether you want to bolster your help desk or provide 24/7 customer support, how you intend to use ChatGPT or Bard will play a massive role in determining which product is best for your company. We tested the performance of ChatGPT vs. Google Bard in seven crucial areas to help you make your decision.
Summarizing content for research
Conducting research is a time-consuming process, so having a tool that can do it for you and summarize the main takeaways is a considerable advantage. Google is already an expert at scanning search results to give users the best resources, so it’s no surprise that Bard excels at this task. Bard users only need to provide a link to an article and ask for a summary, and Bard handles the rest.

The free version of ChatGPT is more limited. It can’t summarize articles from a link, so users must copy and paste the full text. ChatGPT assigns tokens to each prompt, which essentially limits the number of words you can include. One token can be equivalent to either one character or word, and each search is limited to 4,096 tokens. So, if your article exceeds roughly 3,000 words, you’ll likely need to use ChatGPT Plus to get a response.
ChatGPT Plus can access web pages from a link, and plugins like WebPilot can enhance its ability to summarize content. ChatGPT Plus was able to break the article down into four key sections and identify the main takeaways.

Crafting contextual emails or conversations
Aside from assisting you with research, ChatGPT and Bard can also help you with interpersonal communication. For example, if you need an extension on a project you’re working on, generative AI can write an email to your manager that includes the proper context.
As you’ll see below, Bard wrote a concise email addressing the deadline and explaining why the due date needed to be adjusted.

ChatGPT also accomplished the task, generating a subject line and an email that addressed the same prompt. However, the response was far wordier than Bard’s and included redundant information.
OpenAI built ChatGPT using a technique known as prompt engineering, which lets the AI adapt to the cues within a conversation to understand the user’s intent. That means it might take multiple revised prompts before ChatGPT can provide you with the desired result.

Bard and ChatGPT also maintain the context of your conversations, so you can revisit past prompts to gain additional assistance with minimal effort. Say your manager follows up with you about the project extension and asks for additional information.
Bard created a response to the manager’s inquiry and remembered that the project was an article on ChatGPT and Bard. It took some liberties regarding why the project is behind schedule, but the new message is coherent.

ChatGPT also provided a detailed response that maintained the context of the conversation and even proposed solutions to possibly avoid this situation in the future.

Curating info on current events
One of the most significant differences between ChatGPT vs. Bard is each product’s ability to deliver accurate and up-to-date responses. The free version of ChatGPT can’t access information beyond September 2021. So if you wanted information concerning current events, like the recent wildfires in Canada, you’d need to pay for the premium version.
ChatGPT Plus can use its internet access to provide users with real-time information on the state of the wildfires. It confirmed that the fires were still ongoing at the time the question was asked, and it provided related questions the user might want to ask to get more details.

Bard can provide precise data on the state of world events in real time. When asked about the Canadian wildfires, Bard delivered accurate information and also offered additional context regarding the causes of the fires and what had been affected.

Creating text for new content
One of the most talked-about functions of generative AI is creating original content. ChatGPT and Bard can write fictional stories, informational blog posts, and test questions. Generative AI uses machine learning to understand the intent behind prompts and give users better responses. When we asked ChatGPT to craft a fifth-grade level multiplication word problem, it did it and provided instructions for how to solve it.

When Bard saw the same question, it generated two similar word problems with instructions for how to solve them. It also provided the answers and showed its work—unlike ChatGPT.

Rewriting text to update existing content
If you have an extensive collection of content in your blog or knowledge base, editing and revising content can become a time-consuming job. While AI struggles to create complete articles that are search engine optimized and accurate without human edits, people want to know how efficiently it can handle revisions.
We asked Bard to update an older blog post on self-service best practices to improve readability. Bard approached the task by breaking each section down into scannable lists. From a visual standpoint, Bard succeeded but lost context in the process. It couldn’t tell the difference between recommendations and the explanation behind each recommendation.
For example, the Bard revision claims all help centers should support over 40 languages. But the article clearly states that businesses should strive to support customers in their own language, and uses the Zendesk help center as an example of supporting over 40 languages. Bard delivered three drafts for the prompt, but they all had similar issues.

ChatGPT preserved the paragraph structure of the original post and reduced the length of each section. The revised content can still stand to be improved, with some sentences being unnecessarily wordy. But overall, it did a good job of preserving the intent behind the original piece.

Writing code
Coding is similar in practice to writing content, but the outcome is more objective to judge. Either the code works, or it has bugs. When we asked ChatGPT to write JavaScript for a tic-tac-toe application, it provided code for a basic 2D format. The code produced zero errors when tested in OnlineGDB.
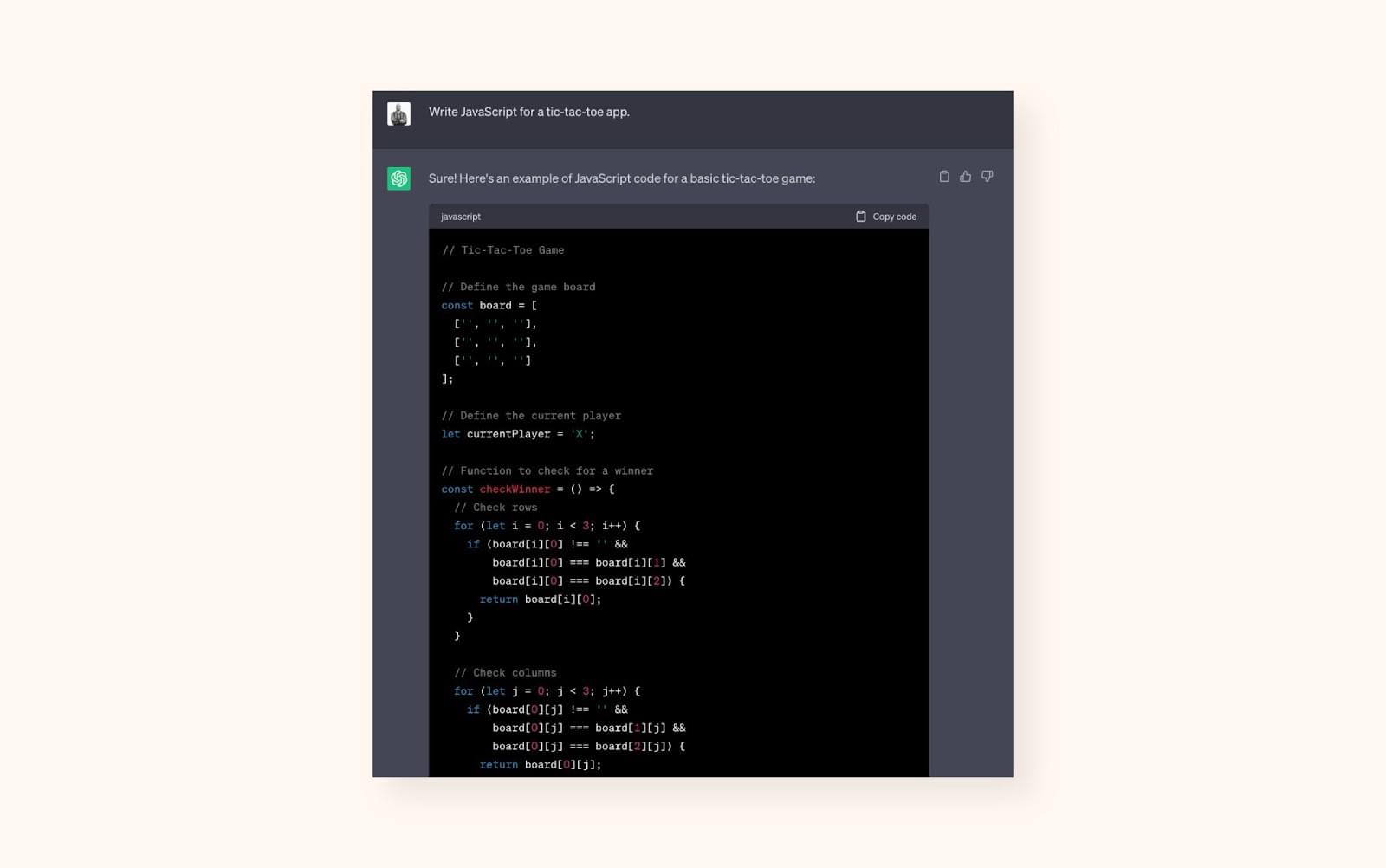
Bard received the same prompt and again provided three drafts of code. One draft had additional CSS and HTML code to round out the JavaScript. Each draft of code produced similar errors when tested, indicating that Bard users may need to put in additional effort before they have a working product.

Generating image results
One of the key differences between Google Bard vs. ChatGPT is the ability to incorporate images into responses. Despite its human-like responses, the basic version of ChatGPT is still essentially an AI chatbot limited to text. If you ask it for image results, it will only type out a description.
ChatGPT Plus can use plugins to incorporate image results. When we asked it to show art by painters like Vincent van Gogh, it produced five paintings that it considered similar in style.

Bard can access Google image search to provide users with image results within the platform. If you were to conduct an image search on your own, the results wouldn’t be exactly the same.
When we asked Bard to share art by painters like van Gogh, it did so—and even generated two sentences describing each artist. When we entered the same command in a Google image search, the results were primarily images of van Gogh’s work.

Use AI to control costs
Keeping costs down without sacrificing the quality of your customer service is a difficult balancing act, but AI can help. Learn how to strategically implement AI tools in your support processes to drive cost savings while improving your CX.
ChatGPT vs. Bard pricing
ChatGPT offers two plans. The basic version is free, but users may only use 4,096 tokens per message. ChatGPT Plus costs $20 per month and provides users with access to new features and plugins, faster response times, and priority access during peak periods. ChatGPT Plus users are limited to 100 messages every four hours, without a token limit.
Google Bard is free for everyone with an eligible Google account. Users can send an unlimited number of messages per day. It’s unclear if Google intends for Bard to remain free in the future or if it will evolve into a tiered plan structure.
Pros and cons of Bard and ChatGPT
The tests we ran to compare Bard vs. ChatGPT are a small sample representing a broad range of potential applications. It’s important to note that both AI products are works in progress, and their capabilities change quickly. For example, when Bard launched earlier this year, it was powered by LaMDA, and by May, it upgraded to PaLM 2, which significantly enhanced its performance.
Refer to the list of pros and cons below for greater context regarding why you might choose one product over the other.
Is ChatGPT or Bard better for your business?
This comparison between ChatGPT vs. Bard reveals that each product has applications to make life easier. But at this point, neither can be used as a customer-facing tool on its own, presenting limitations.
If you need a solution that can improve your customer experience, it’s best to pursue one designed specifically for that purpose. Zendesk can provide your business with the tools it needs to optimize performance and drive revenue. And no need to worry about missing out on the latest AI technology—Zendesk AI has an OpenAI API to help you deliver a more intelligent customer experience while saving time and money.
